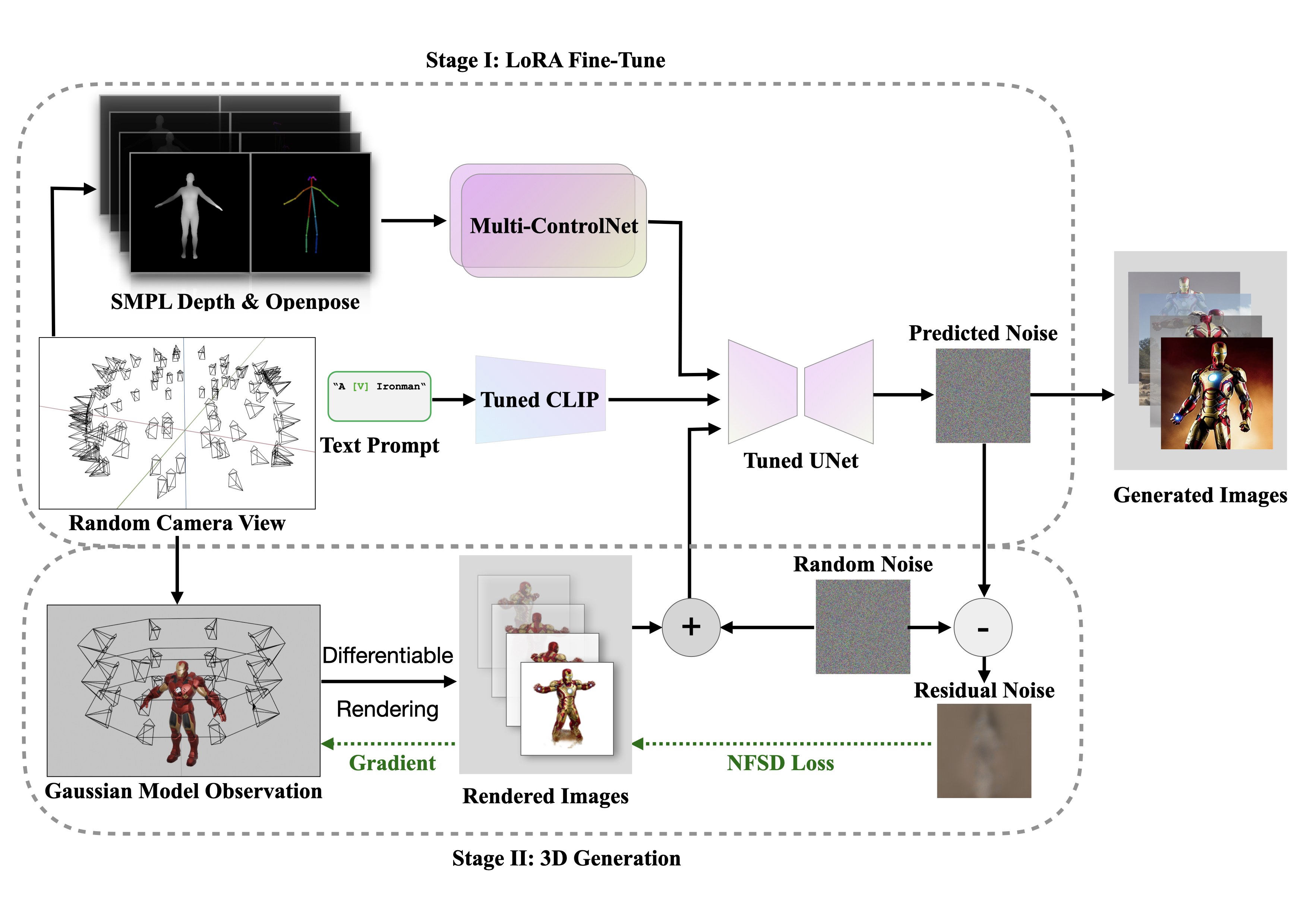
Fig 1: Two-Stage Training Methodology
Introduction
The field of digital 3D content creation, crucial in gaming, advertising, and the emerging MetaVerse, requires efficient and sophisticated tools for generating 3D characters. This blog post delves into an innovative approach that integrates ControlNet and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) into existing text-to-image diffusion models, offering a solution to common issues like spatial inconsistency and multi-view artifacts in multi-view image synthesis.
Gallery
3D Model Examples
 |  |  |
|---|
Pose Reference Images
| Ref Image | Openpose | Generated 3D Model |
|---|---|---|
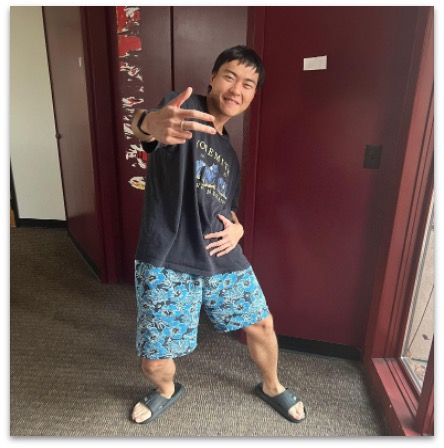 |  |  |
Training Process

Methodology
Pipeline Overview
The methodology comprises three core components:
- Stable Diffusion Fine-Tuned with LoRA: Uses Stable Diffusion for detailed image generation from text inputs. LoRA fine-tunes this model for character-specific features.
 Samples from Fine-Tuned Stable Diffusion
Samples from Fine-Tuned Stable Diffusion
ControlNet for Multi-View Consistency: Ensures consistent character appearance from various angles using 3D body pose estimation and rendering 2D poses in random viewpoints.
Generative Gaussian Splatting: Transforms multi-view images into a cohesive 3D model, synthesizing spatial relations and depth cues.
3D Representations
3D information is represented through a set of 3D Gaussians. These are defined by parameters like center, scaling factor, rotation quaternion, opacity, and color.
Text-to-3D Generation
The core process involves Score Distillation Sampling (SDS), optimizing 3D Gaussians against various camera poses and rendering RGB and transparency views.
Noise-Free Score Distillation (NFSD)
NFSD isolates distortion-related components from predicted noise in the diffusion process, enhancing the optimization efficiency.
Results and Analysis
3D Generation Process
The 3D generation process is illustrated through various training steps, highlighting the progressive development of the model.

Fig 3: 3D Generation Process at Different Steps
Challenges and Future Directions
While the approach shows promising results, challenges like lengthy generation times and the need for high-quality training sets were encountered. Future directions include leveraging CUDA programming for faster depth map generation and experimenting with multiple viewpoints rendering.